What is CO₂e?
Understanding Carbon Dioxide Equivalent and Its Impact on Climate Change
With the growing urgency to tackle climate change, terms like carbon footprint, greenhouse gases (GHGs), and CO₂e are becoming more common in discussions around sustainability. But what exactly is CO₂e, and why is it important?
In this blog, we’ll break down what CO₂e (carbon dioxide equivalent) means, how it helps measure climate impact, and why it is a crucial metric for businesses, governments, and individuals working toward carbon reduction.
1. What is CO₂e?
CO₂e stands for carbon dioxide equivalent, a standardised unit used to express the impact of different greenhouse gases (GHGs) in terms of carbon dioxide (CO₂), the most well-known greenhouse gas.
While CO₂ is the most abundant GHG emitted by human activities, other gases—such as methane (CH₄), nitrous oxide (N₂O), and fluorinated gases—also contribute to global warming. However, these gases have different warming potentials, meaning some trap significantly more heat in the atmosphere than CO₂.
To compare their effects fairly, scientists convert their warming impact into a CO₂-equivalent value, which is expressed as CO₂e.
2. Why Do We Use CO₂e?
Measuring emissions in CO₂e provides a more comprehensive and accurate picture of climate impact by accounting for all greenhouse gases in a single number. This helps with:
Comparing the impact of different gases
Since methane (CH₄) has about 28 times the warming potential of CO₂ over a 100-year period, emitting 1 ton of methane is equivalent to 28 tons of CO₂e.
Setting climate targets
Governments and businesses use CO₂e to set carbon reduction targets and report emissions. For example, the UK’s goal to reach net zero by 2050 is based on total CO₂e emissions.
Simplifying carbon footprint calculations
Instead of tracking individual gases separately, CO₂e allows people to calculate their total impact in a single, easy-to-understand metric.
3. The Greenhouse Gases Included in CO₂e
The most commonly measured greenhouse gases that contribute to CO₂e calculations include:
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
Source: Fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, cement production
Methane (CH₄)
Source: Agriculture (livestock, rice paddies), landfill waste, natural gas leaks
Nitrous Oxide (N₂O)
Source: Fertilisers, industrial activities, combustion
Fluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF₆)
Source: Refrigerants, air conditioners, electronics manufacturing
By converting these emissions into CO₂e, scientists, policymakers, and companies can create consistent, comparable reports that help guide climate action.
4. CO₂e in Everyday Life: What Does It Mean for Individuals?
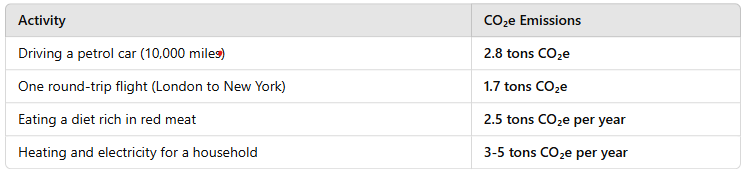
The average person’s carbon footprint is measured in CO₂e. In the UK, the average per capita carbon footprint is about 10 tons of CO₂e per year.
Here’s how different activities contribute to an individual's CO₂e emissions:
Switching to greener alternatives—such as electric vehicles, renewable energy, plant-based diets, and energy-efficient homes—can significantly reduce an individual’s CO₂e footprint.
5. Reducing CO₂e: The Role of Businesses and Governments
To achieve global climate targets, businesses, governments, and individuals must work together to cut CO₂e emissions.
Net Zero Targets
Many countries have pledged to reach net zero CO₂e emissions by 2050 to meet the Paris Climate Accord targets. This requires:
Switching to renewable energy (solar, wind, hydro)
Improving energy efficiency in buildings and transport
Reducing methane emissions from agriculture and waste
Enhancing carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies
Corporate Carbon Reduction
Businesses are under increasing pressure to measure and reduce their CO₂e impact. This includes:
Conducting carbon audits to track emissions
Offsetting carbon through reforestation and carbon credits
Switching to low-carbon supply chains
Sustainable Construction and Housing
Since buildings contribute nearly 40% of global emissions, the housing sector plays a key role in reducing CO₂e. Companies like Environmentools help housebuilders:
Measure and reduce embodied and operational carbon
Track and report sustainability efforts with ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) metrics
Implement low-carbon building materials and renewable energy solutions
These tools make it easier for developers to build eco-friendly, low-carbon homes that benefit both the environment and homeowners' finances.
6. Conclusion: Why CO₂e Matters for the Future
Understanding CO₂e is essential for tackling climate change. It provides a standardised way to measure the impact of all greenhouse gases, helping individuals, businesses, and governments take meaningful action.
By tracking CO₂e emissions, we can:
✅ Make informed decisions about sustainability
✅ Set clear climate targets and policies
✅ Reduce our impact on the planet
Whether it’s switching to renewable energy, adopting green building practices, or simply making smarter lifestyle choices, every step toward reducing CO₂e counts.
Take Action Today!
Want to know how you can reduce your CO₂e footprint? Visit Environmentools to learn how innovative tools can help businesses and homeowners track, measure, and lower their carbon impact.